Program EnRoute using Gateway API
Introduction
EnRoute is an Ingress API Gateway that is built using Envoy proxy. EnRoute has an extremely simple configuration model to help connect and secuire microservices at Ingress.
The Gateway API is an upcoming standard that is a replacement for Ingress. Like Ingress, it is an attempt to describe networking for traffic entering the Kubernetes cluster.
EnRoute Ingress API Gateway is now compliant with the Gateway API standard v0.6.0. In a Kubernetes cluster, EnRoute can now listen for Gateway API artifacts.
In this article, we discuss how Gateway API can be used to program EnRoute Ingress Controller API Gateway.
We start with a simple example to introduce Gateway API capabilities. Subsequent articles in this series, with include more details depending on how our customers adopt and use it.
Gateway API Example
Prerequisites
- This example needs a Kubernete cluster 1.23 or up
- Gateway API does not need a service mesh. We use a simple non-mesh cluster to demonstrate it.
- EnRoute version
v0.13.0-b1or later that has support for Gateway API
EnRoute helm charts
EnRoute can be easily configured using helm charts. To demonstrate gateway-api capabilities, a special chart called gateway-api is created. The following helm charts are available
| Chart | Description |
|---|---|
enroute | Use this chart to configure and install EnRoute Ingress API Gateway |
demo-services | Use this chart to install workloads used to demo EnRoute (eg: httpbin, grpcbin) |
service-globalconfig | Use this chart to configure EnRoute global configuration (eg: Global Rate-Limit Engine Config, Configuration for Mesh Integration, Filters for all traffic - eg: Health Checker, Lua, etc.) |
service-host-route | Use this chart to provide L7 connectivity and policy for a service using a host-and-route (GatewayHost) or just a route (ServiceRoute) |
gateway-api | Use this chart to configure EnRoute using Gateway API |
Add enroute helm repo
add the helm chart -
helm repo add saaras https://charts.getenroute.io
check repositories -
helm search repo
name chart version app version description
saaras/demo-services 0.1.0 0.1.0 Chart for Workloads used in EnRoute demo - http...
saaras/enroute 0.8.0 v0.12.0 EnRoute API Gateway
saaras/gateway-api 0.6.0 v0.13.0-b1 Configure EnRoute using Gateway API
saaras/service-globalconfig 0.2.0 v0.11.0 Global Config and Global Filters for EnRoute
saaras/service-host-route 0.2.0 v0.11.0 Host (GatewayHost), Route (ServiceRoute) config
saaras/service-policy 0.5.0 v0.12.0 Demo Service L7 Policy using EnRoute API Gateway
Install enroute
helm install enroute-gw-api saaras/enroute \
--set serviceaccount.create=true \
--create-namespace \
--namespace enroute
NAME: enroute-gw-api
LAST DEPLOYED: Wed Jan 18 23:57:18 2023
NAMESPACE: enroute
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
______ _____ _
| ____| | __ \ | |
| |__ _ __ | |__) |___ _ _| |_ ___
| __| | '_ \| _ // _ \| | | | __/ _ \
| |____| | | | | \ | (_) | |_| | || __/
|______|_| |_|_| \_\___/ \__,_|\__\___|
𝙴𝚗𝚁𝚘𝚞𝚝𝚎 Ingress API Gateway Community Edition Installed!
-------------------------------------------------------
Request a free evaluation license for enterprise version
by sending an email to contact@saaras.io
Slack Channel - https://slack.saaras.io
Getting Started Guide - https://docs.getenroute.io/docs/prologue/introduction/
EnRoute Docs - https://docs.getenroute.io/
EnRoute Features - https://getenroute.io/features/
kubectl get all -n enroute
name ready status restarts age
pod/enroute-5b4d45ff6c-mzv4b 3/3 running 0 16m
name type cluster-ip external-ip port(s) age
service/enroute loadbalancer 10.43.91.42 212.2.242.227 80:30808/tcp,443:31920/tcp 16m
name ready up-to-date available age
deployment.apps/enroute 1/1 1 1 16m
name desired current ready age
replicaset.apps/enroute-5b4d45ff6c 1 1 1 16m
Install demo services
kubectl create namespace echo
kubectl create namespace httpbin
kubectl create namespace grpc
kubectl create namespace avote
helm install demo-services saaras/demo-services
kubectl get svc --all-namespaces
namespace name type cluster-ip external-ip port(s) age
default kubernetes clusterip 10.43.0.1 <none> 443/tcp 2d21h
kube-system kube-dns clusterip 10.43.0.10 <none> 53/udp,53/tcp,9153/tcp 2d21h
enroute enroute loadbalancer 10.43.91.42 212.2.242.227 80:30808/tcp,443:31920/tcp 20d
echo echo clusterip 10.43.137.85 <none> 9001/tcp 21s
httpbin httpbin clusterip 10.43.104.4 <none> 9000/tcp 21s
grpc grpcbin clusterip 10.43.56.47 <none> 9002/tcp 21s
We will use Gateway API to expose the service httpbin externally. Next we create a self-signed certificate which we can use to serve traffic over https.
Create TLS secret for use in Gateway API
Create a self-signed certificate
openssl req -nodes -new -x509 -keyout server.key -out server.cert
create kubernetes secret using self-signed certificate
kubectl create secret tls tlscert -n httpbin --key="server.key" --cert="server.cert"
The tlscert created in the step above is used in the gateway api example helm chart
Expose httpbin service using Gateway API
helm install gateway-api-example saaras/gateway-api
Edit EnRoute service to direct traffic to Gateway API Listener
kubectl edit -n enroute service enroute
We will cover the configuration using Gateway API below, but the listener we defined in the Gateway uses port 8444. Traffic from the LoadBalancer EnRoute service, should be directed to this port. Set targetPort to 8444 to direct encrypted traffic from the external Load Balancer to this Gateway API defined listener.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
...
name: enroute
namespace: enroute
spec:
clusterIP: 10.43.50.156
ports:
...
- name: https
nodePort: 31326
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8444
...
app.kubernetes.io/name: enroute
type: LoadBalancer
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- hostname: 7c51d516-1e1d-462b-a116-f22f191bf387.lb.managedk8s.com
ip: 212.2.242.227
Send test traffic
curl -s -k https://hello-gateway.saaraslabs.com/get
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Host": "hello-gateway.saaraslabs.com",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.68.0",
"X-Envoy-Expected-Rq-Timeout-Ms": "15000",
"X-Envoy-Internal": "true"
},
"origin": "192.168.1.4",
"url": "https://hello-gateway.saaraslabs.com/get"
}
Understanding Gateway Artifacts
The helm chart creates the following artifacts
- A
GatewayClassobject - common configuration related to multipleGateways, which is defined per-cluster - A
Gatewaythat definesListenerthat is the entry point for traffic and L7 routing HTTPRoutethat defines L7 routing rulesHTTPRoute.Spec.backendRefthat defines the services to which the traffic is destined.
GatewayClass
A GatewayClass object defines state that can be used by several Gateways
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: GatewayClass
metadata:
...
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
name: enroute
...
spec:
controllerName: saaras.io/enroute
description: The gateway class for enroute
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2023-01-18T00:25:17Z"
message: Valid GatewayClass
observedGeneration: 1
reason: Valid
status: "True"
type: Accepted
kubectl get gatewayclasses.gateway.networking.k8s.io --all-namespaces
NAME CONTROLLER ACCEPTED AGE
enroute saaras.io/enroute True 40h
Gateway
A Gateway defines listeners to receive incoming traffic from the external Load Balancer.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
...
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
name: enroute
namespace: httpbin
...
spec:
gatewayClassName: enroute
listeners:
- allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
name: gw-ingress-http
port: 8081
protocol: HTTP
- allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: All
hostname: hello-gateway.saaraslabs.com
name: gw-ingress-https
port: 8444
protocol: HTTPS
tls:
certificateRefs:
- group: ""
kind: Secret
name: tlscert
mode: Terminate
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "1970-01-01T00:00:00Z"
message: Waiting for controller
reason: NotReconciled
status: Unknown
type: Accepted
HTTPRoute
A HTTPRoute can be used to provide L7 routing rules to reach a service defined in Kubernetes
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
annotations:
...
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
name: gatewayapi-httproute
namespace: httpbin
...
spec:
hostnames:
- hello-gateway.saaraslabs.com
parentRefs:
- group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
name: enroute
rules:
- backendRefs:
- group: ""
kind: Service
name: httpbin
namespace: httpbin
port: 9000
weight: 1
matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /status
- backendRefs:
- group: ""
kind: Service
name: httpbin
namespace: httpbin
port: 9000
weight: 1
matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /get
Conclusion
Teams using EnRoute can continue to work with a simpler configuration model on their projects. When teams are ready for additional complexity arising from Gateway API, they can transition easily. This is possible since EnRoute’s flexibility provides an ability to work with simpler API, and evaluate Gateway API without any operational overhead.
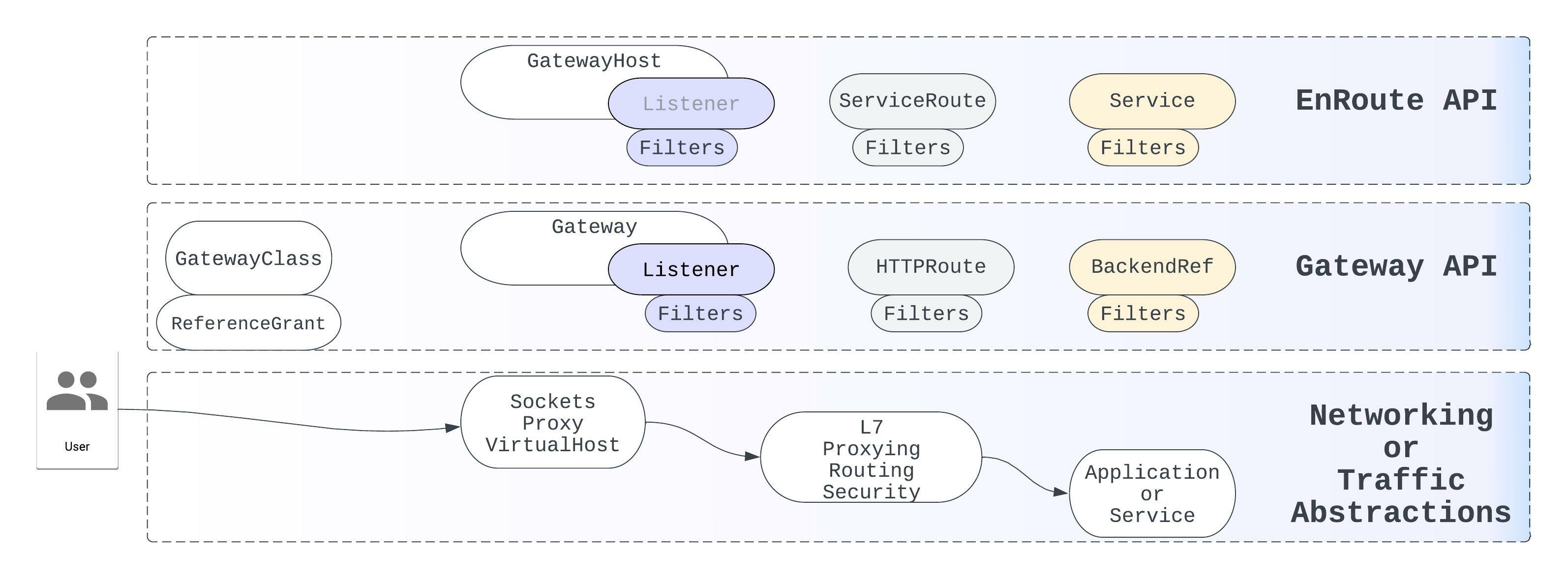
Gateway API abstractions are similar to EnRoute and resemble EnRoute model closely. EnRoute architecture was defined years back to provide an easy-to-use interface for Ingress, when Ingress was just released and it’s capabilities were limited.
EnRoute architecture allows for working with Gateway API and EnRoute API concurrently. Abstractions defined using any of the API can be mixed and matched to achieve the desired behavior and program the underlying Envoy proxy. This is possible since Gateway API configuration model resembles the EnRoute config model.
Gateway API assumes roles like platform operator, cluster operator, developer and uses ReferenceGrant, GatewayClass and Gateway to define cross-namespace access-control using them. We will discuss them in a subsequent article. While EnRoute supports these custom resources, they are not covered here for simplicity.
EnRoute is feature rich and is validated for stablity. All the development done on EnRoute, its features can be configured using EnRoute’s config model and will work with Gateway API. The current version of EnRoute supports the latest v0.6.0 of Gateway API as of writing this.